Poll Question Splash Page
This Week's Anatomy Quiz
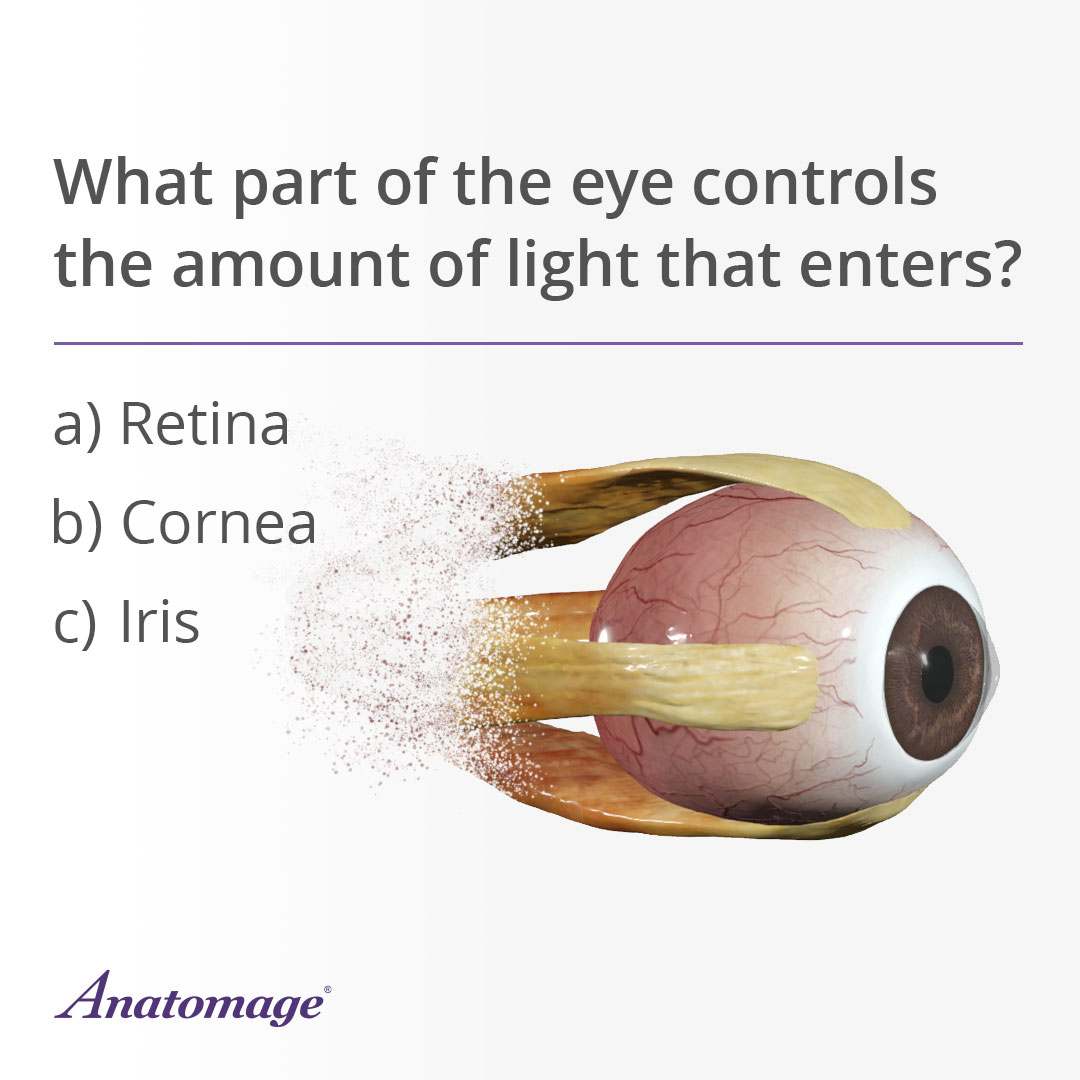
Answer:
c) Iris
The iris, the colored part of your eye, controls how much light enters by adjusting the size of the pupil: It gets smaller in bright light and larger in the dark to help you see clearly.
Fun fact: Iris patterns are unique and differ from person to person, just like fingerprints!
Anatomy Quiz Archive
Roll over or click on the archived quizzes to see the answers.
Answer:
a) Pancreas
The pancreas plays a vital role in controlling blood sugar by producing the hormone insulin. Insulin moves glucose from your bloodstream into your cells, where it’s used for energy.
Fun fact: The pancreas is technically part of both the digestive system and the endocrine system; it produces enzymes to help digest food and hormones to regulate blood sugar.
Answer:
a) Ilium
The ilium is the largest of the three bones (alongside the pubis and ischium) that are fused together to form the hip bone. The ilium serves to bear weight and help support the spine.
Fun fact: The human ilium’s shape allows our gluteal muscles to attach at points that keep the body balanced and stable when walking. In fact, scientists can tell if an ancient species walked on two legs by looking at its ilium — shorter, broader ilia are an indication of bipedalism.
Answer:
b) 11
The 11 major systems are the Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous, Endocrine, Cardiovascular, Lymphatic, Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary, and Reproductive systems.
Fun fact: Chronic stress can affect every system. It can slow digestion, weaken immunity, increase heart rate, mess with hormones, and even shrink the brain.
Answer:
b) Heart
The respiratory system enables your body to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. The trachea, or windpipe, acts as the main airway, carrying air from the nose and mouth into the lungs, where it branches into the bronchi. These tubes direct air into each lung so oxygen can reach the deeper parts of the respiratory system.
Fun fact: Your left bronchus is narrower and longer because it has to curve around the heart, which slightly tilts into the left lung space.
Answer:
a) Jejunum
The jejunum is the middle section of the small intestine, located between the duodenum (first) and the ileum (final). It plays a critical role in digestion by absorbing nutrients like sugars and amino acids from food. Its inner walls are lined with circular folds and tiny hair-like projections called villi for better absorption.
Fun fact: The jejunum makes up about 40% of the small intestine — it’s packed into your abdomen and could stretch to about 8 feet when uncoiled.
Answer:
a) Cervical
Located in the neck, the cervical spine is the uppermost part of the spinal column. It supports your head, protects your spinal cord, and allows for a wide range of head and neck movement. However, despite its flexibility, the cervical spine is also highly vulnerable to injury due to its location and mobility.
Fun fact: Both humans and giraffes have the same number of cervical vertebrae: seven. (Giraffes’ neck bones are just much longer!)
Answer:
a) Heart rate
An ECG (electrocardiogram) records the electrical signals in your heart that trigger heartbeats. Each heartbeat produces a wave pattern, and the ECG can track the timing between waves, thus calculating your heart rate.
Fun fact: While a normal resting heart rate typically ranges from 60 to 100 bpm, athletes can have lower rates due to stronger heart efficiency — as low as 30 bpm!
Answer:
c) Pituitary gland
This pea-shaped endocrine gland sits behind the bridge of your nose, below the hypothalamus; it’s responsible for the production and release of several hormones that contribute to important bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, and response to stress.
Fun fact: The pituitary gland is often referred to as the “master” gland because it controls the function of many other glands in the endocrine system.
